Thread Weight Chart: Decoding Thread Weights for Sewing Success
Thread is the unsung hero in the world of sewing, quilting, and fashion design. It binds the fabric together, creating magic in every stitch. However, the weight of the thread, especially cotton thread, often determines the quality and durability of the final piece. Understanding thread weight can transform the way professionals approach their projects, leading to superior craftsmanship and a polished finish.
Unraveling the Thread Weight Mystery
Thread weight is crucial in sewing projects, affecting everything from seam strength to visual appeal. Polyester thread offers numerous benefits, including strength and versatility, making it ideal for diverse sewing projects. In sewing and quilting, the thread weight impacts not only the aesthetic but also the functionality of the finished product. For fashion designers, the right thread can make the difference between a garment that lasts and one that falls apart after a few wears. In machine embroidery, selecting appropriate thread weights is essential for achieving high-quality results, considering factors like fabric type and machine compatibility. Knowing which thread to use for different applications can streamline production and enhance results, making it an essential topic for sewers, fashion designers, and quilters alike.
The purpose of this guide is to shed light on the various thread weights available, their applications, and how they influence the outcome of sewing projects. By the end of this article, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of how to select the right thread weight for their needs, enhancing both the look and durability of their creations.
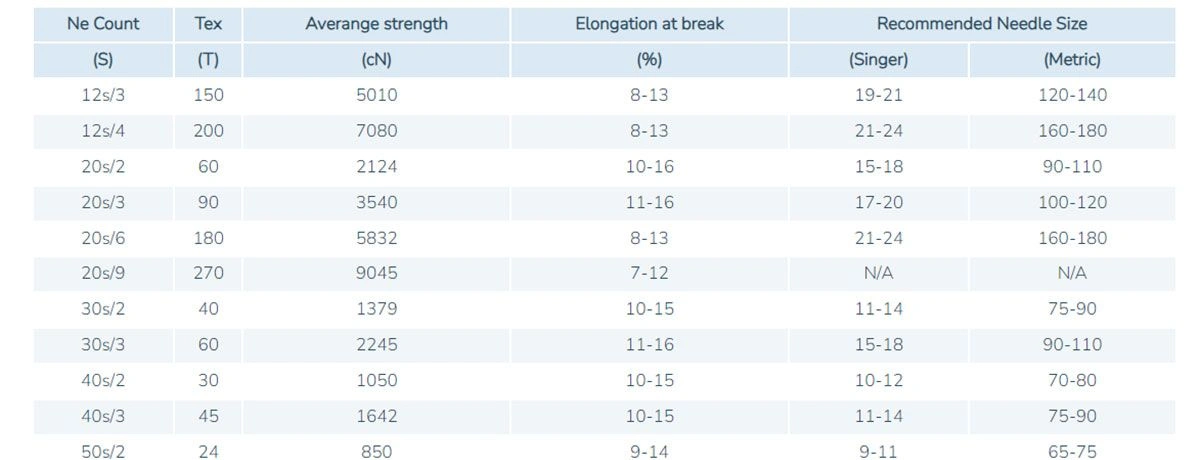
The Standard Thread Weight System
Thread weights are categorized using a numeric system that indicates the thickness of the thread. Thread measurements refer to the thickness of the thread strand, with larger numbers indicating thinner threads, which can be confusing due to historical inconsistencies in terminology between thread and needle sizes. The lower the number, the thicker the thread, and vice versa. For instance, a 30wt thread is thicker than an 80wt thread. This system helps sewers determine which thread will best fit their project needs. It’s important to note that different countries may have varying standards, but the principle remains the same.
Understanding this numbering system is crucial for selecting the correct thread. Thread size, such as the commonly used 50wt thread, impacts sewing projects by providing a balance between strength and subtlety, making it ideal for piecing quilts. In contrast, a 40wt thread might be preferred for quilting as it adds texture and durability to the seams. For embroidery enthusiasts, thicker threads like 30wt can create bold designs, while thinner threads like 60wt are ideal for intricate details.
Selecting the Perfect Thread for Your Sewing Project
Choosing the right thread weight can be daunting, but a few guiding principles can simplify the process. Bobbin thread is essential for embroidery tasks that require a fine, strong, and often inconspicuous thread. For garment construction, a 50wt thread is typically suitable for general sewing, providing a smooth finish without adding bulk. However, when working with lightweight fabrics, an 80wt thread can prevent seam bulk, allowing for a cleaner look. Conversely, heavier materials require a 30wt thread to ensure seam durability and strength.
When it comes to embroidery, the thread’s weight plays a significant role in the design’s outcome. A thick embroidery floss or thread, such as 30wt, is perfect for bold, standout designs, while a 60wt thread allows for more delicate and detailed work. Thicker thread weights, such as 30/40, enhance the visibility of stitches and add texture to projects. For quilting, thread weight can affect both the piecing and quilting stages. A 50wt thread is ideal for piecing, offering strong seams without overpowering the fabric design, while a 40wt thread adds dimension and texture to the quilting stitches. Cotton threads, particularly 50wt, are resilient and thin, preventing bulkiness in seams and improving the overall quality of quilting.
Thread Weight and Fabric Type
Thread weight plays a crucial role in determining the compatibility of a thread with a specific fabric type. Different fabrics require different thread weights to achieve the best results. For example, delicate fabrics such as silk, chiffon, or organza require fine threads (60-100wt) to prevent visible stitches and maintain the fabric’s texture. Medium-weight fabrics like cotton, linen, or rayon can use medium-weight threads (40-50wt) for general sewing and quilting. Heavy-duty fabrics like denim, canvas, or upholstery require heavier threads (12-30wt) to withstand the fabric’s thickness and density. Stretchy fabrics like knits or spandex require threads with some give, such as polyester or cotton-polyester blends, to prevent thread breakage.
When choosing a thread weight for a specific fabric type, consider the fabric’s thickness, texture, and intended use. This will ensure that the thread blends well with the fabric and produces the desired stitch quality. Matching the right thread weight to the fabric type not only enhances the visual appeal but also ensures the durability and functionality of the finished product.
Thread Weight and Tension
Thread weight can significantly impact the tension of a sewing project. Thicker threads tend to produce more tension, while finer threads produce less. This is because thicker threads have a larger diameter, which can cause the thread to pull more tightly on the fabric. Heavier threads (12-30wt) can produce more tension, which can be beneficial for projects that require a lot of stability, such as quilting or home decor. Medium-weight threads (40-50wt) produce a moderate amount of tension, making them suitable for general sewing and quilting. Fine threads (60-100wt) produce less tension, making them ideal for delicate fabrics, hand-sewing, or projects that require a soft, flexible finish.
To adjust tension when using different thread weights, consider the following:
-
Use a longer stitch length to reduce tension with thicker threads.
-
Use a shorter stitch length to increase tension with finer threads.
-
Adjust the machine’s tension settings according to the thread weight and fabric type.
-
Use a walking foot or even feed foot to help manage tension and prevent thread breakage.
By understanding the relationship between thread weight and tension, you can achieve better stitch quality, reduce thread breakage, and produce professional-looking results in your sewing projects.
The Influence of Thread Weight on Final Products
The weight of the thread affects not only the appearance but also the durability of the finished product. Thin threads, defined as those of 50 wt. and thinner, are typically 2-ply and are used for a refined and delicate finish. Thicker threads, like a 30wt, can add texture and visual interest, making them suitable for decorative stitching and topstitching. However, they can also create bulk, which may not be ideal for all projects. Thinner threads, such as 70wt or 80wt, offer a more refined and delicate finish, perfect for heirloom sewing and fine garments.
Choosing the right thread weight can significantly influence the feel of the fabric. A thick thread for embroidery can create a tactile and visually stimulating design, while a lightweight sewing thread can provide a seamless finish that blends into the fabric. The durability of the final product is also impacted by thread weight; thicker threads often mean stronger seams but may require adjustments to machine tension and needle size.
Thread Weight and Sewing Techniques
Thread weight has a profound impact on both machine and hand sewing techniques. For machine sewing, selecting the appropriate thread weight is crucial for machine quilting, as it affects the quality of stitches and the overall appearance of the quilt. Adjusting the tension and selecting the appropriate needle size is crucial when working with different thread weights. Thicker threads require larger needles and may necessitate tension adjustments to prevent breakage and ensure smooth stitching. Additionally, the impact of thread weight on the performance of a sewing machine cannot be overstated, as high-quality threads prevent buildup and ensure smooth operation.
In hand sewing, choosing the right thread weight can affect the ease of stitching and the final appearance. Thicker threads may require more effort to pull through the fabric, whereas thinner threads glide effortlessly but may require additional strands for strength. It’s important to match the thread weight with the fabric type and stitch style to achieve the best results.
Case Studies in Thread Weight Application
Case 1: Quilting with Different Thread Weights
A quilt project demonstrated the impact of using a 50wt thread for piecing and a 40wt for quilting. Using a thinner thread helps to minimize seam bulk, which is particularly beneficial in quilting. The 50wt thread provided strong, seamless connections between fabric pieces, while the 40wt thread added depth and texture to the quilting stitches. This combination resulted in a durable quilt with a visually appealing finish, showcasing how thread weight can enhance both function and aesthetics.
Case 2: Embroidered Jacket Design with Polyester Thread
An embroidered jacket design highlighted the contrasting effects of using a 30wt thread for bold designs versus a 60wt thread for detailed work. Using the correct weight thread, such as 40wt or 60wt, is crucial for achieving the desired quality and appearance in bold embroidery designs. The 30wt thread allowed for vibrant, eye-catching embroidery that stood out against the fabric. In contrast, the 60wt thread produced intricate, delicate designs that required less machine stress and reduced stitching time. This case study illustrates how thread weight can dramatically alter the visual impact of embroidery.
Case 3: Garment Construction with Lightweight and Heavy Fabrics
A garment construction project showcased the benefits of using an 80wt thread for lightweight fabrics. This choice minimized seam bulk, resulting in a smooth, polished finish. Additionally, using polyester threads for heavy-duty garment construction ensures enhanced strength and durability. Conversely, a 30wt thread was used for heavier materials, providing the necessary strength and durability for long-lasting wear. This example underscores the importance of matching thread weight to fabric type for optimal results.
Summary and Next Steps
Understanding the different weights of thread is a crucial aspect of sewing, quilting, and fashion design. The right thread weight can elevate a project, enhancing its appearance, feel, and durability. By considering factors such as fabric type, project purpose, and desired visual effect, sewers can make informed decisions that lead to outstanding results.
This guide has provided insights into the various thread weights available and their applications, offering practical advice for selecting the appropriate thread for any project. Readers are encouraged to experiment with different thread weights and share their experiences in the comments section below. For those seeking further guidance, consulting a professional or joining a sewing community can provide valuable support and inspiration.
In conclusion, mastering thread weight selection is an essential skill for any sewer, quilter, or fashion designer. By understanding how thread weight affects the final product, individuals can create pieces that are not only beautiful but also durable and functional. With this knowledge, the possibilities in the world of sewing are endless.
